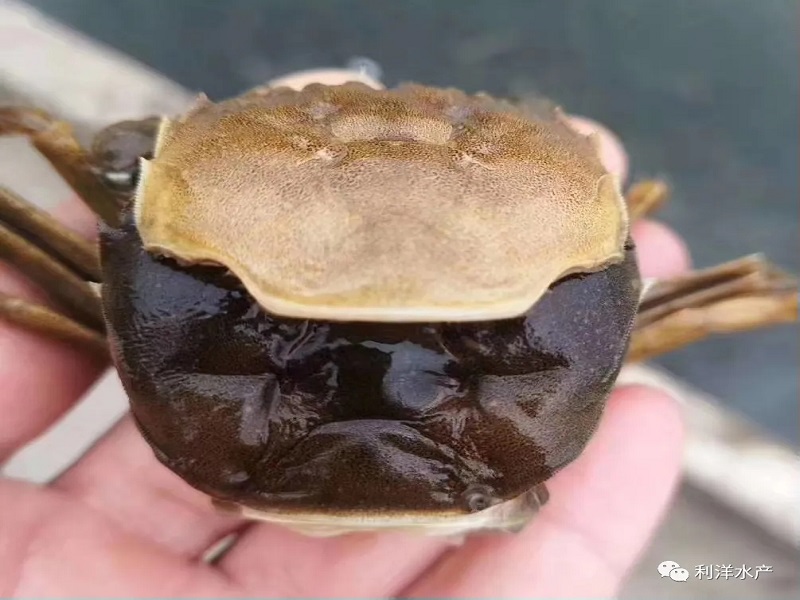
Shelling is very important for river crabs. If river crabs are not shelled well, they will not grow well. If there are many foot pulling crabs, they will die due to shelling failure.
How do river crabs shell? Where did its shell come from? The shell of river crab is secreted from the dermis epithelial cells under it, which is composed of upper epidermis, outer epidermis and inner epidermis. It can be roughly divided into shelling interval, early stage, late stage and subsequent stage.
The time required for crab to molt varies with individual size. The smaller the individual, the faster the molt. Usually, it takes about 15-30 minutes to molt smoothly at a time, and sometimes even 3-5 minutes to molt the old shell. If the molting process fails, the molting time will be prolonged, or even die due to failure.
The new crab is black in color, soft in body and pink in claw foot hair. It is used to calling it "soft shell crab". Therefore, in the process of molting and shortly after molting, river crabs have no ability to resist the enemy, which is a dangerous moment in their life. Before and after the river crab sheds its old shell, it is necessary to increase the calcium content in the water body. Potassium dicarboxylate and calcium propionate are poured out. 30.1% ionic calcium is convenient for the river crab to absorb and improve the blood calcium concentration.
Key points of management during molting period:
During the shelling interval, the crab shell calcifies and absorbs calcium and trace elements. The river crab will eat a lot, accumulate energy materials and trace elements, and prepare materials for shelling.
- 1) Two days before and after each molting, sprinkle 150g / mu of active calcium polyformate in the evening to increase the content of calcium ions in the water. The content of calcium ion of active polyformate is ≥ 30.1%. It is completely water-soluble and easy to absorb. It can increase the hardness of water body, increase the blood calcium concentration of river crab and promote hard shell. At the same time, the active calcium polyformate is added to the feed regularly. The free formic acid can inhibit the reproduction of harmful bacteria in the digestive tract, improve the absorption and utilization rate of feed nutrition and promote feeding.
- 2) During molting, the water level needs to be kept stable, and generally there is no need to change water. Improve the survival rate of river crab molting.
- 3) The feeding area and molting area must be differentiated. It is strictly prohibited to put bait in the molting area. If there are few aquatic plants in the molting area, more aquatic plants should be added and kept quiet.
- 4) When visiting the pond in the early morning, if you find soft shell crabs, you can pick them up and put them in a bucket for temporary storage for 1 ~ 2 hours. After the river crabs absorb enough water and can climb freely, they can be put back into the original pool.
Post time: May-24-2022